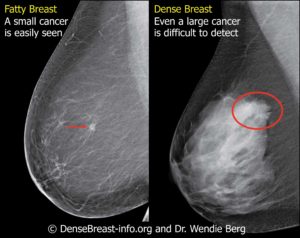
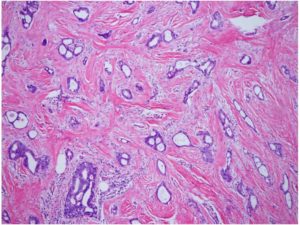
In one study, gynecologists estimated that a woman whose mammogram was positive had a higher than 80 percent chance of having breast cancer; the reality is that her chance is less than 10 percent. Of course, women who have a positive mammogram often undergo other tests, such as an MRI and a biopsy, which can offer more precision about the presence of cancer. But researchers have found that even after the battery of exams, about 5 of every 1,000 women will have a false-positive result and will be told they have breast cancer when they do not.
The confusion has serious consequences. These women are likely to receive unnecessary treatment — generally some combination of surgery, radiation or chemotherapy, all of which have serious side effects and are stressful and expensive. Switzerland and France, grasping this problem, are halting and reconsidering their mammogram programs. In Switzerland, they’re not screening ahead of time, preferring to manage cases of breast cancer as they’re diagnosed. In France, doctors are letting women decide for themselves whether to have the tests.
Read the full article at the Washington Post.